At YSH Group, we specialize in the OEM and private label manufacturing of premium probiotic supplements. Whether you need capsules, powders, or custom blends, our GMP-certified facilities and R&D team ensure top-tier quality and global delivery.
👉 Ready to build your probiotic product line? Contact us here or explore our capabilities at yshherb.com.
Strain Selection Activity Guarantee Encapsulation Technology
Market Reality Check
The global probiotic market continues to be hot, but behind the boom, there are hidden traps that can destroy your brand reputation and consumer trust.
1. Strain Selection: Scientific Verification is the Only Passport
The efficacy of probiotics is highly dependent on specific strains and their clinical verification.

Key Point 1: Recognize the “Strain ID”
- Reject vague information such as “Lactobacillus” and “Bifidobacterium”
- Mandate suppliers provide full strain numbers (e.g., Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG® (LGG®), Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12®)
- Verify authorization documents from strain patent holders (e.g., Chr. Hansen, DuPont, etc.)
Key Point 2: Efficacy Must Be Well-Documented
- Request clinical studies on target efficacy (e.g., immune modulation, intestinal health, feminine care)
- Confirm strain research population matches target market (Asian, European, and American populations have different intestinal flora)
- Beware of “all-purpose strain” marketing claims
Key Point 3: Compliance with Global Regulations
- China: Must be listed in “Strains that can be used in food” and comply with “Probiotic health food declaration and review regulations”
- USA: Follow FDA GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) certification
- EU: Must comply with EU Novel Food regulations or have QS qualification
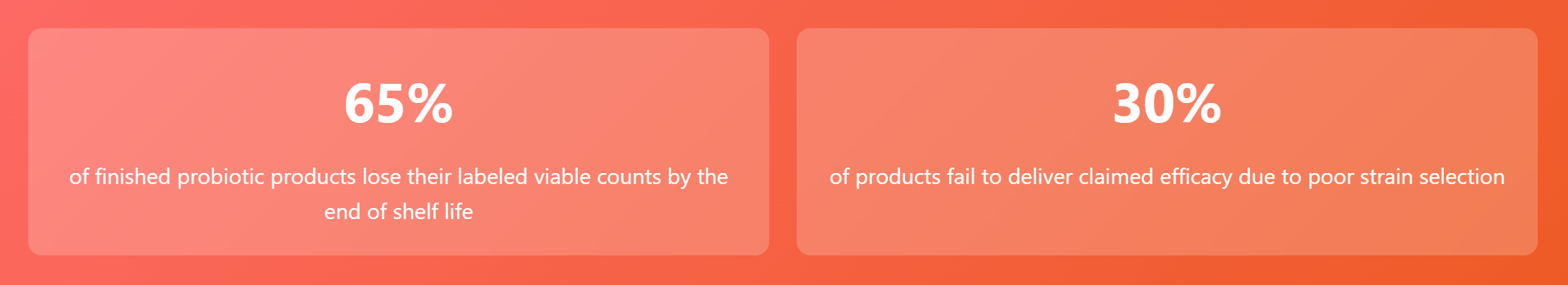
2. Activity Assurance: The Battle for Survival from Production to Intestines
Probiotics are fragile living organisms – high temperature, humidity, oxygen, and stomach acid can all lead to massive bacterial death.
Key Point 1: “Activity Protection” at the Production End
- Lyophilization: Inquire about freeze-drying equipment grade and process control precision (residual moisture content is key).
- Low-oxygen/oxygen-free environment: Is core mixing conducted under nitrogen protection? Are environmental oxygen monitoring data available?
- Stability test data: Request shelf-life viable bacteria decay data under target storage conditions (e.g., 25°C/60%RH) in actual packaging.

Key Point 2: Packaging Material is the “First Line of Defense”
- High-barrier packaging: Prefer double aluminum blisters or aluminum-plastic composite pouches
- Critical examination: Review oxygen transmission rate (OTR) and water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) test reports
- Light-proof design: UV rays accelerate bacterial death
- Desiccant integration: Ensure controllable humidity inside packaging
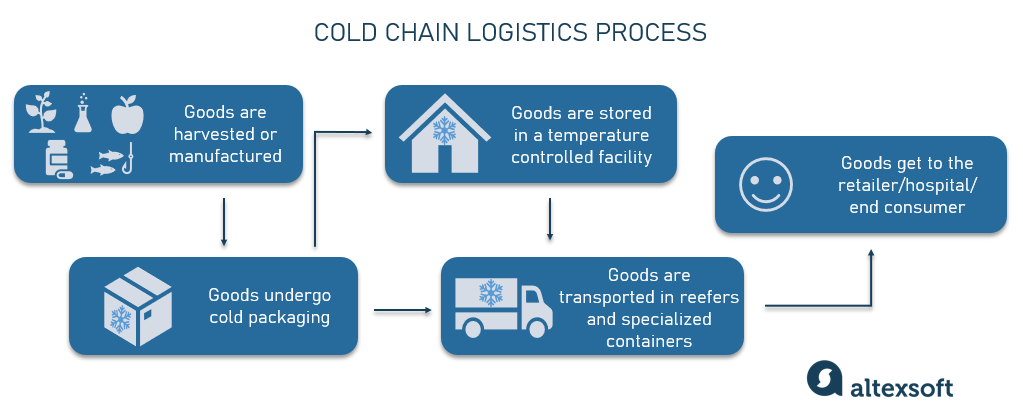
Key Point 3: Cold Chain and Stability Commitment
- Clarify if complete cold chain (2-8°C) is required throughout distribution
- If “room temperature stability” is claimed, OEMs must provide accelerated tests (e.g., 37°C) and long-term real shelf-life data
- Require third-party endorsement: end-of-shelf-life viable bacteria count reports from international labs (e.g., SGS, Eurofins)
3. Encapsulation Technology: Breaking Through the “Invisible Armor” of Stomach Acid
Gastric acid (pH 1.5-3.5) is the fatal barrier – unprotected strains often have less than 20% gastric acid survival rate



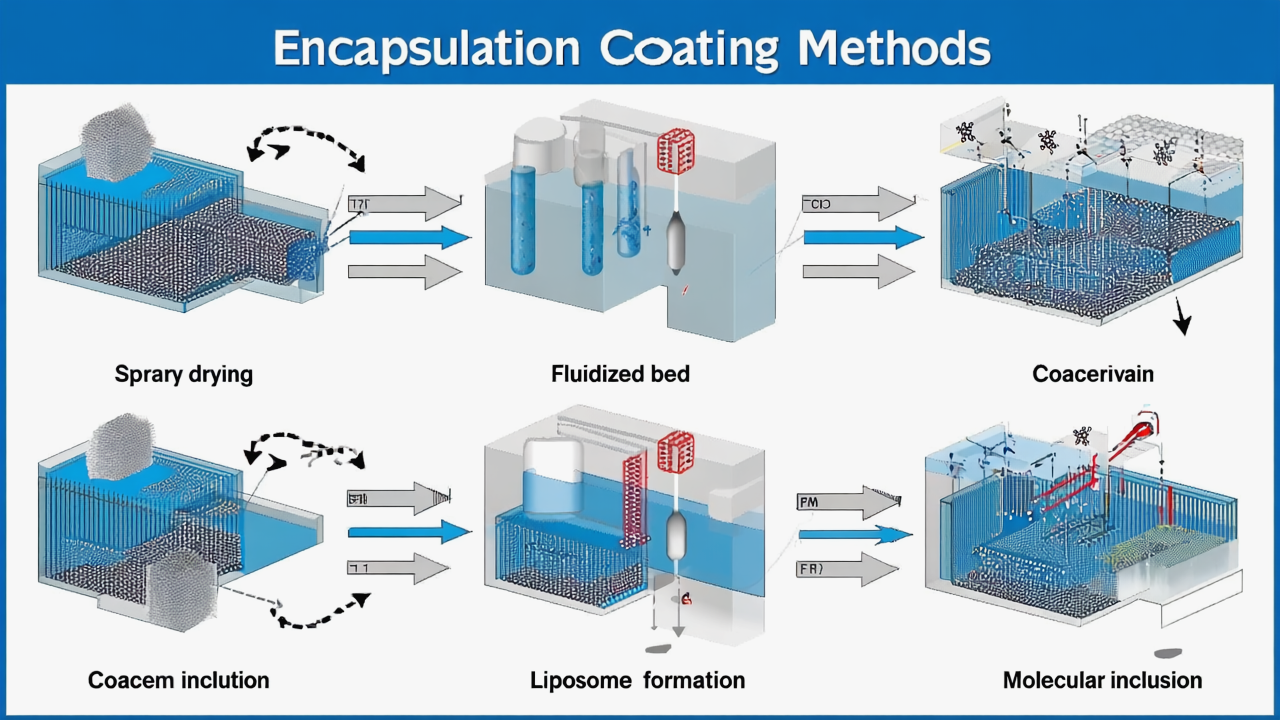
Key Point 2: Compatibility of Packaging Materials and Encapsulation Technology
- Enteric coats may be affected by high temperature and humidity
- Evaluate stability under selected packaging materials and storage conditions
- Confirm encapsulation process doesn’t affect final product disintegration time
Key Point 3: Cost and Regulatory Compliance
- High-end encapsulation technology significantly increases costs – balance efficacy with pricing strategy
- Ensure encapsulation materials comply with food additive regulations in target markets
- China: GB 2760 | USA: FDA 21 CFR | EU: E-number system
4. Selecting Professional OEM: Avoiding Systemic Risks
Comprehensive evaluation criteria for choosing the right manufacturing partner



Your Brand’s Lifeline Depends on the Right Choice
Choosing a probiotic OEM partner is choosing the guardian of your brand’s lifeline. Any compromise on strain science, activity guarantee, and encapsulation technology will directly weaken your product’s efficacy, cause consumer complaints, and create compliance risks.
We are not just OEMs – we are committed to being your scientific backbone and compliance engine to conquer the global probiotic market together.

Visit our website and get it touch
www.yshherb.com